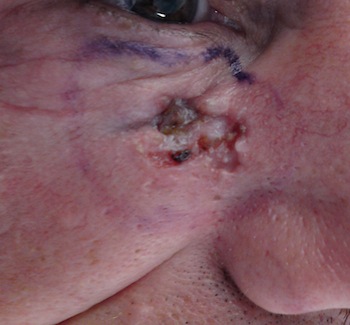
Basal cell carcinoma starts in the top layer of the skin called the epidermis. It grows slowly and is nearly always painless. A new skin growth that bleeds easily or does not heal well may suggest basal cell carcinoma. The majority of these cancers occur on areas of skin that are regularly exposed to sunlight or other ultraviolet radiation. They may also appear on the scalp. Basal cell skin cancer used to be more common in people over age 40, but is now often diagnosed in younger people.
Your risk for basal cell skin cancer is higher if you have:
- Fair skin
- Blue or green eyes
- Blond or red hair
- Overexposure to x-rays or other forms of radiation
Basal cell skin cancer almost never spreads. But, if left untreated, it may eventually grow into surrounding areas and nearby tissues and bone.
Click here to download the patient information sheet produced by the British Association of Dermatologists
Appearance:
Basal cell carcinoma may look only slightly different from normal skin. The cancer may appear as skin bump or growth that is:
- Pearly or waxy
- White or light pink
- Flesh-Coloured or brown
- In some cases the skin may be just slightly raised or even flat.
Symptoms:
A skin sore that bleeds easily
A sore that does not heal
Oozing or crusting spots in a sore
Appearance of a scar-like sore without having injured the area
Irregular blood vessels in or around the spot
A sore with a depressed (sunken) area in the middle
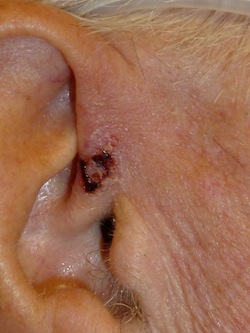
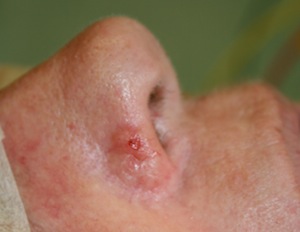
BCCs can usually be found on the sun exposed parts of the face such as:
in front of the ear...
on the nose...
on the eyelid...
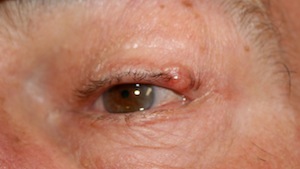
or on the cheek...